Business Model Innovation: How Blackberry Reinvented Itself
How Blackberry went from having less than 1% smartphone market share to being an automobile software market leader.

A business model is simply the way in which a business creates and captures value through its daily operations. A company’s business model has many different dimensions explained in the video below. Business model innovation is when a business decides to significantly change how it creates and captures value.
Similar to the different schools of thought pertaining to innovation, the current body of knowledge differentiates between two types of business model innovation. A company could choose to incrementally change their business model over a period of time or it could opt for a more revolutionary approach by ‘instantly’ changing its business model. The former involves gradual changes in some elements of a business model whereas the latter involves a change in the business as a whole.
Research by Mezger conceptualised business model innovation as a distinct dynamic capability. He defined dynamic capability as a firm’s ‘capacity to sense opportunities, seize them through the development of valuable and unique business models, and accordingly reconfigure the firm’s competencies and resources.’ During the business model innovation process it is important to identify key market signals to determine if the changes to elements in your business are desirable and sustainable in the constantly changing marketplace. This leads us to ask “what triggers business model innovation”?
Triggers of Business Model Innovation
If it is not broken, why fix it? This saying is also true about business models. If there were no reasons to change how a company creates and captures value, there would be no reason for business model innovation. However, in the business environment, the only constant thing is change: new ventures disrupt markets, technology advancements and changing consumer needs and preferences usually trigger business model innovation as companies need to adapt or risk their competitive edge.
Research states that triggers for Business model innovation can be either internal or external. Some common internal triggers are client needs, client feedback lost sales and organizational characteristics. On the other hand, common external triggers are new technologies, digitization, price changes, customer behaviour, external stakeholders, environmental factors, market crises or financial pressure.
Enablers of Business Model Innovation
So what can entrepreneurs do to ensure business model innovation is a success? Well, the organisational structure is integral to business model innovation. Research suggests that the more complicated and hierarchical the organizational structure the more difficult it is for firms to innovate their business models. Entrepreneurs also need to be willing to change the way they run their businesses. The agile organisational structures prevalent in startups historically enable them to implement decisions and pivot their enterprises quicker than larger organisations with more complex structures. Other business model innovation enablers include market sensing and marketing channel selection. Entrepreneurs need to prioritize consistently scanning the market for any changes and new ways to reach customers. The more knowledgeable a business is about its market the easier it will be to innovate its business model.
Barriers to Business Model Innovation
Business Model Innovation requires overcoming certain barriers. According to research, business leaders may encounter Cognitive barriers due to bias (they believe their current business model does not require change), and lack of managerial know-how pertaining to business model innovation.
Research by Lopez categorizes barriers into; institutional, market, organizational, behavioural and technological. The institutional barriers are caused by restrictive & outdated institutional policies. Market barriers refer to lack of information, monopolies and relative cost of labour. Organizational barriers are attributed to poor business strategy, financial constraints and fragmented management systems. Behavioural barriers are caused by employees’ lack of attention, lack of perceived control and lack of information. The technological barriers are caused by factors associated with the technical know-how, the cost of technology and being unable to support technology.
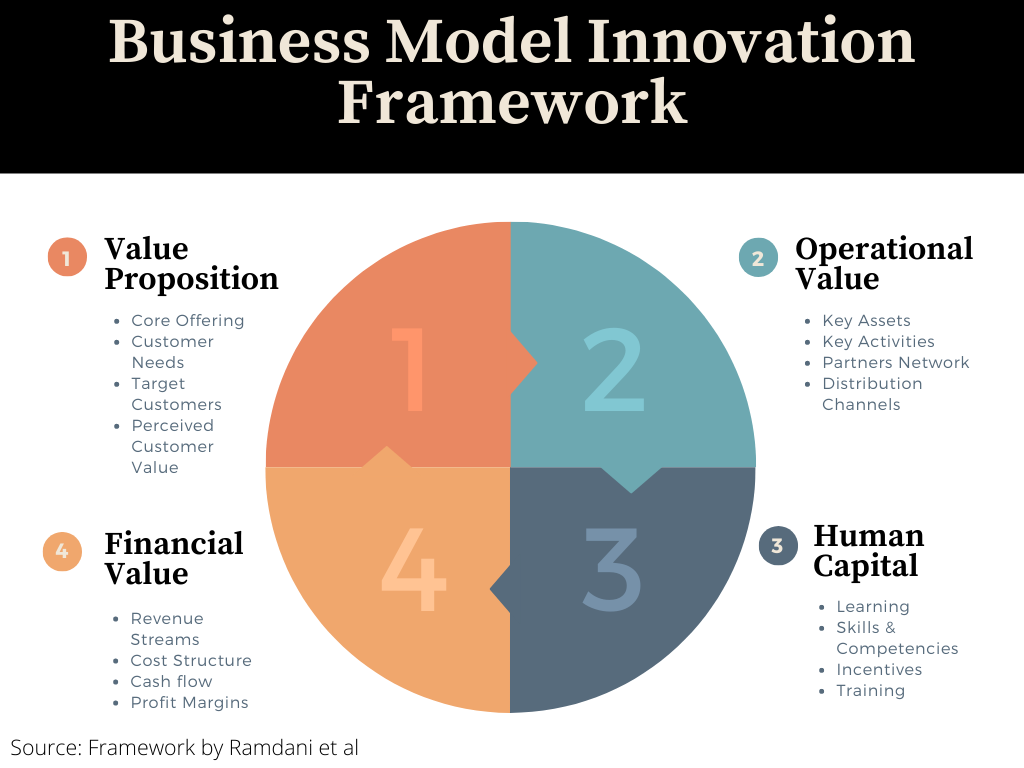
A Business Model Innovation Framework
Despite being the market leader for smartphones in 2010, Blackberry failed to innovate and consequently got usurped by Apple and Samsung in the smartphone industry. Although it failed in product innovation (failing to add relevant features for changing consumer needs), I believe Blackberry is an excellent case study of business model innovation. The template provided by Boumedienne Ramdani gives us a useful tool to analyse how Blackberry transitioned from a Smartphone market leader to an intelligent security software market leader. Blackberry now provides operating software to more than 195 million cars worldwide.
Value proposition: These elements include transforming what a company sells, exploring new customer needs, acquiring target customers and determining whether the benefits offered are perceived by customers. Sometimes due to certain triggers, companies may need to change their value proposition. For example, Blackberry needed to change its value proposition due to shifts in the competitive mobile industry. As suggested by the Washington Examiner, Blackberry failed to adapt to the potential threat of the iPhone, launched in 2007, which promised more entertainment, quality pictures, and apps to consumers. By 2017, Blackberry’s market share had plummeted to less than 1% of the mobile phone market, according to Gartner. After unsuccessfully competing in the market, Blackberry announced it would not support its mobile devices on January 4 2022. Its focus had changed to using its core competencies to build the software to power cyber security worldwide. Look at Blackberry’s ‘new’ value proposition stated in its annual reports: “The Company’s goal is to offer smarter security solutions that are more effective, require fewer resources to support and produce a better return on investment for customers than competing offerings. To achieve this vision, the Company continues to extend the functionality of its AI-focused BlackBerry Spark software platform and safety-certified QNX Neutrino real-time operating system and is commercializing its new BlackBerry IVY™ intelligent vehicle data platform.”
Operational value: These elements include configuring key assets and sequencing activities to deliver the value proposition, exposing the various means by which a company reaches out to customers, and establishing links with key partners and suppliers. Blackberry needed to acquire different assets and form new partnerships to deliver its new value proposition. Blackberry had to prioritise investing in AI technology and forming partnerships with car manufacturers and other organisations handling sensitive data in the same way Microsoft had to form strategic partnerships with manufacturers in the computer industry.
Human capital: This refers to establishing new ways of doing business, and developing the skills and competencies needed for the new business model through motivating and involving individuals in the innovation process and acquiring fresh talent. It is evident that Blackberry needed to acquire new talent and equip its workforce with new skills. Blackberry’s current leadership team is filled with executives possessing a lot of experience in IoT and cybersecurity. Furthermore, Research & Development is performed by a highly skilled designated workforce.
Financial value: These elements include activities linked with how to capture value through revenue streams, price-setting, and evaluating the financial viability and profitability of a business. Blackberry’s revenue model and cost structure radically changed because of its business model innovation. Blackberry generates revenue from licensing its software and Intellectual property, subscriptions, and consulting fees. When Blackberry was still focused on smartphones, revenue was generated from once-off product sales. According to Blackberry’s 2022 annual report, gross profit margins are healthy across its different segments: 59.3% for Cybersecurity, 83.1% for IoT, and 63.5% for licensing and other services.
Concluding Remarks
I have the honour of helping aspiring and early-stage entrepreneurs develop their business models and a few issues arise when discussing value propositions and resources. It is very important to be clear about what resources you will need and what new value you are creating when innovating your business model: if you are unclear about what resources you need to create new products and services, it could lead to an unsuccessful business model. Therefore before innovating your business model, answer these questions:
Is your product/service demand declining?
What market trends are worth your time & resources?
What skills and resources are needed to capitalise on those trends?
What is your competence gap (i.e. the difference between your current skills and the required new skills)?